
WHY HIGH PRESSURE OXYGEN IS USED IN BOMB CALORIMETERS
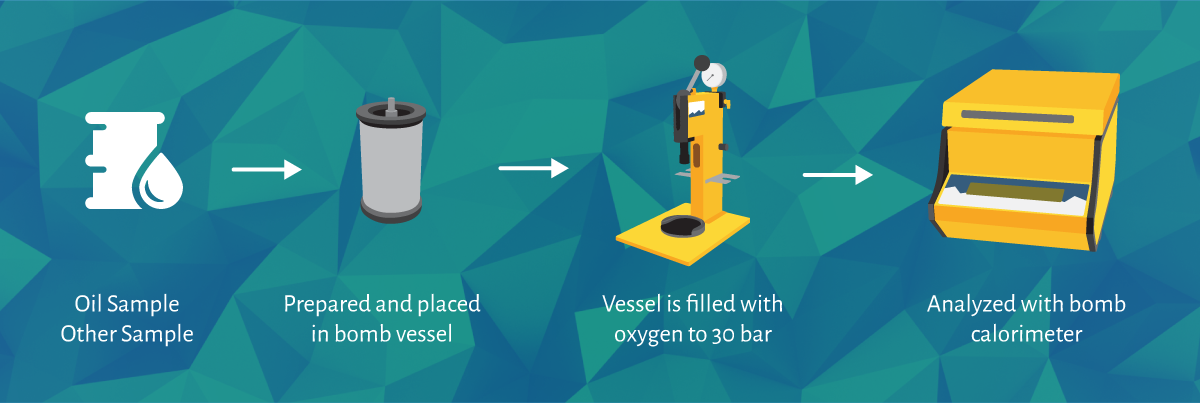
Oxygen Bomb Calorimeters (also known as Constant Volume Calorimeters) are used for various applications in different industries to calculate the heat released from a combustion reaction (also known as a combustion calorimeter), the calorific value of the sample, be it any solid or liquid substance like coal and oil, is then measured.
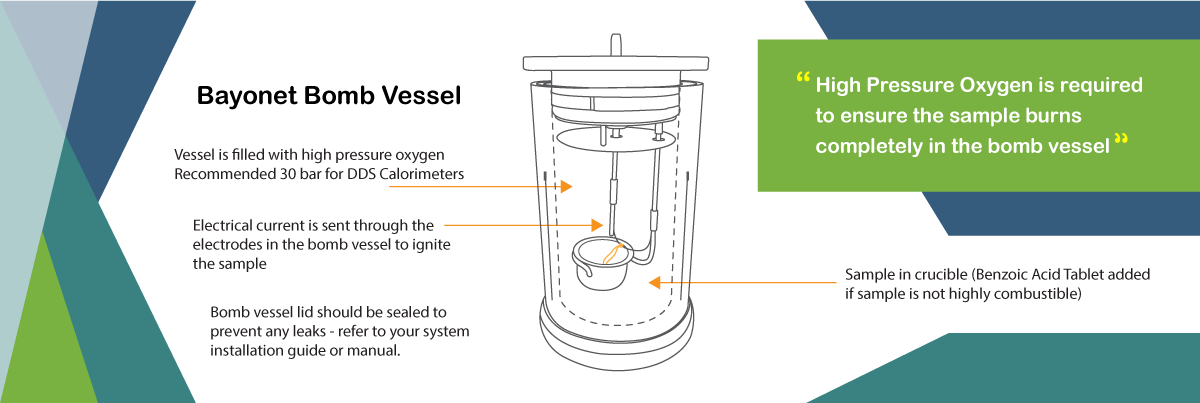
It is known as a constant volume calorimeter as it holds the constant volume and the oxygen at any given pressure (at DDS Calorimeters, we use up to 30 bar).
The sample used for the calorific value determination is prepared and measured, then placed into the vessel and sealed with the quick thread lid/screw lid. The sample is then ignited with an electrical current in the oxygen atmosphere.
The rise in the temperature is then measured to determine the heat released during the combustion of the sample.
The DDS Calorimeters range automatically calculates the calorific value of the sample, eliminating the need for manual calculations from the operator.
DURING SAMPLE ANALYSIS
High Pressure Oxygen is required to ensure the sample burns completely in the bomb vessel. For an accurate final result, we recommend using a pressure of 30 bar in the CAL3K Calorimeters to ensure complete burning of the sample.
The older CAL2K bomb vessels require 10 to 20 bar for complete combustion, but a pressure of 30 bar is recommended for all our oxygen bomb vessels to ensure complete combustion.
In special circumstances, the oxygen pressure can be reduced.
HIGHLY COMBUSTIBLE SAMPLES
In some applications where highly combustible samples are being analysed, nitrogen is used instead of oxygen (at a low pressure), for example when burning highly combustible explosives. (See Explosives Analysis Application).
If water is formed during the combustion of the sample this will result to another reason for using high pressure oxygen in a bomb calorimeter. The excess oxygen pressure assists with the formation of water in the bomb vessel.

HIGH PRESSURE OXYGEN USE PRECAUTIONS
WARNING:
Use caution when working with high pressured oxygen. Ensure all safety precautions are taken when installing your oxygen filling station and that the vessel is filled correctly to 30 bar. Make sure the oxygen supply is secure and that no leaks occur when filling the bomb vessel. If any leaks are detected, consult your agent, or contact us for assistance on correctly setting up the filling station and its components. High Pressure Oxygen can be dangerous if not handled correctly. Always make sure that the vessel is sealed correctly before filling with oxygen (refer to the installation guide or maintenance manual for details). Never attempt to open a bomb vessel before de-filling it (removing all the oxygen from the vessel).

HIGH PRESSURE OXYGEN REGULATORS
A High Pressure Oxygen Regulator is used with the DDS Calorimeters range and is fitted to the oxygen supply when installing the system for the first time to ensure that the correct pressure of oxygen is supplied to the filling station or calorimeter (if using the CAL3K-AP Calorimeter). The regulator is an absolute MUST when installing the system. For the operator's safety and lab safety, it must be fitted to the oxygen supply. It is an integral part of the complete calorimeter system when it comes to filling the bomb vessel with oxygen before a determination. If a vessel is not filled, it could affect the combustion process within the bomb vessel during a determination, and therefore affect the result of the analysis.
CONCLUSION
Various components and consumables are used during an analysis to ensure the bomb vessel is filled with high pressure oxygen. These components all play a part in analysing samples and the burning of samples within the bomb vessel. The oxygen aids the burning process during combustion to analyse the final calorific value of the sample and assists with a "complete burn" during this process. The oxygen is an integral part of the analysis process.
Applications
Explosives Analysis

Only explosives which can be ignited by heat from the calorimeter's firing circuit can be tested in the oxygen calorimeter. Then very minute/small quantities are used for analysis. The calorific value of an explosive is not very high, but the burning speed is.
Read MoreCoal Analysis

The coal industry is the traditional application of calorimeters because coal has a variety of properties, apart from being black. If the coal is used for steam generation then the calorific value is of paramount importance. The calorific value, short CV, is a measure of how much heat can be extracted from it.
Read MoreOil Analysis

Oils are a non-volatile substance. In general they are not measured frequently because they are very consistent and uniform. Other oil properties are more important than the calorific value, such as taste or viscosity. If an oil is measured in an oxygen calorimeter, then the procedure would be the same as a solid substance.
Read More

